The Department of Defense (DoD) has taken a decisive step to shore up cybersecurity across its vast network of contractors through the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC). This initiative is not just a regulatory hurdle; it is a lifeline for safeguarding sensitive data that underpins national security.
For defense contractors, government agencies, and IT security professionals, understanding the intricacies of CMMC compliance timelines is crucial to staying ahead in a competitive and highly regulated field.

Understanding CMMC: A New Paradigm in Cybersecurity
The concept of CMMC arose from an urgent need to bolster cybersecurity within the Defense Industrial Base (DIB). With cyberattacks becoming increasingly sophisticated, the DoD introduced CMMC as a structured framework to ensure that contractors handling Federal Contract Information (FCI) and Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) meet stringent cybersecurity standards. Unlike previous self-assessed measures, CMMC mandates third-party verification, making it a game changer for defense contractors.
Why CMMC Matters for Defense Contractors
For defense contractors, CMMC is not optional. It's a critical component of doing business with the DoD. Failure to comply can mean losing out on lucrative government contracts. Furthermore, CMMC compliance enhances an organization's reputation, signaling to stakeholders that it prioritizes cybersecurity and data integrity. This trust is invaluable, especially when handling sensitive defense information.
The Role of Government Agencies in CMMC
Government agencies play a pivotal role in the effective implementation of CMMC. Setting clear guidelines and providing necessary resources, agencies ensure that contractors understand their compliance obligations. This collaboration is essential for maintaining the integrity of the defense supply chain, ultimately contributing to national security.
Decoding CMMC Compliance Levels
At the heart of the CMMC framework is a tiered model designed to cater to varying degrees of cybersecurity needs. This model ensures that contractors implement appropriate measures based on the sensitivity of the information they handle.
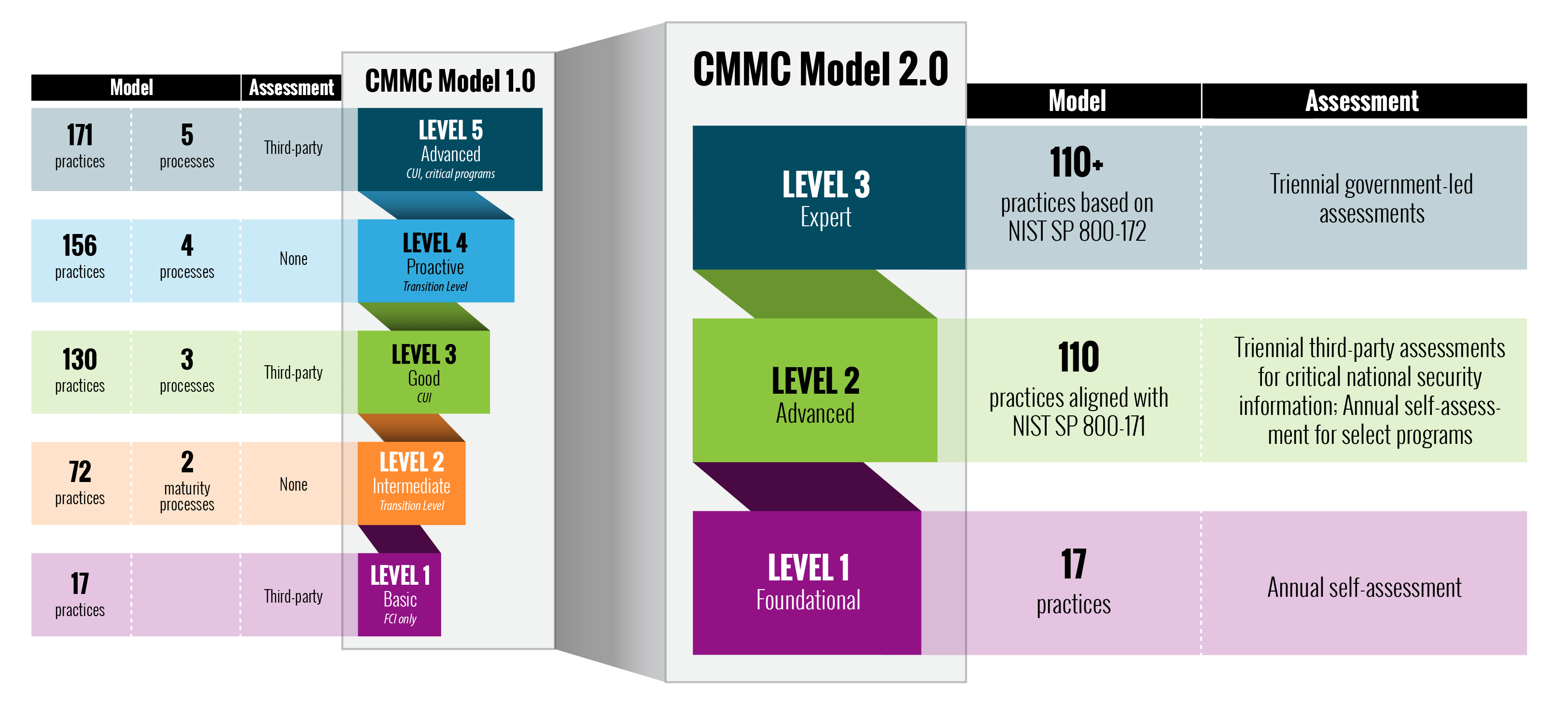
Detailed Overview of CMMC Assessment Levels
The CMMC 2.0 assessment framework simplifies cybersecurity maturity into three levels, tailored to address varying security needs based on the sensitivity of data handled by defense contractors.
Level 1: Foundational
This level requires adherence to basic safeguarding practices for Federal Contract Information (FCI) with 17 specific controls. These practices are generally part of standard business operations, focusing on fundamental cybersecurity measures.
Level 2: Advanced
Aligning with NIST SP 800-171, Level 2 involves implementing a comprehensive set of 110 controls to protect Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). This level necessitates detailed documentation of security policies and processes, ensuring a robust approach to cyber hygiene.
Level 3: Expert
Designed for the most critical environments, Level 3 includes the practices of Level 2 with additional requirements based on a subset of NIST SP 800-172. This top-tier level focuses on ongoing optimization of cybersecurity practices, emphasizing active threat hunting and sophisticated risk management to counter Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs).
These levels ensure that each contractor meets the necessary cybersecurity safeguards relevant to the nature of their contract with the DoD, thereby enhancing the overall security posture within the Defense Industrial Base (DIB).
Differentiating Between FCI and CUI
Understanding the difference between FCI and CUI is paramount for contractors. FCI refers to information provided by or generated for the government under a contract, excluding public data. CUI, however, involves information that requires safeguarding, or dissemination controls pursuant to law or policy. Each type demands distinct protection measures, which are intricately woven into the CMMC framework.
NIST Standards as the Backbone of CMMC
The CMMC framework closely aligns with National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) guidelines, particularly NIST SP 800-171 and NIST SP 800-172. These standards provide a robust foundation for the security requirements prescribed by CMMC, ensuring that contractors employ best practices in cybersecurity.
Navigating the Phased Implementation of CMMC
The CMMC Program will be implemented 60 days after the final Title 48 CFR CMMC acquisition rule is published. It will roll out over three years in a four-phase plan. The process begins with self-assessments in Phase 1 and culminates with complete program implementation in Phase 4. This gradual approach provides time for assessors to receive training and for companies to grasp and apply the CMMC assessment requirements effectively.
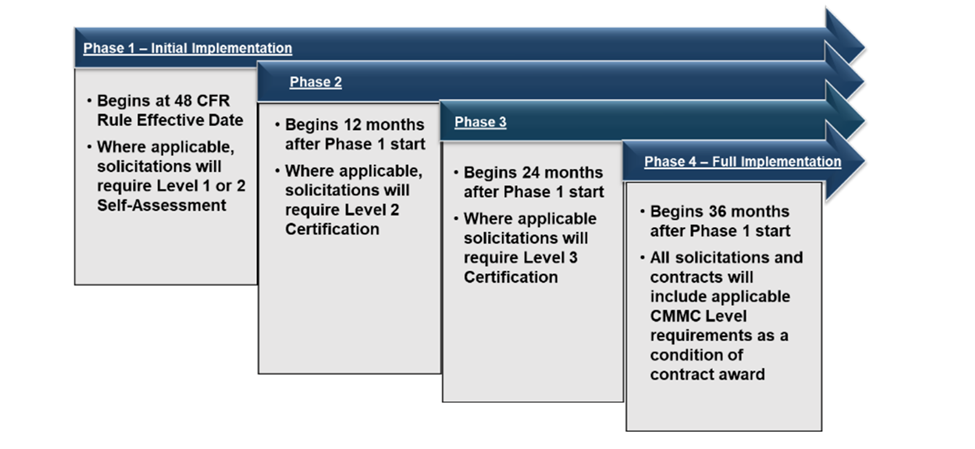
This timeline provides a structured overview for defense contractors to effectively prepare for and achieve CMMC compliance, ensuring their continued eligibility for Department of Defense contracts.
Meeting Deadlines Without Compromise
To successfully meet CMMC deadlines, contractors must develop a comprehensive roadmap outlining their compliance strategy. This includes allocating resources, conducting internal assessments, and collaborating with third-party assessment organizations. Staying ahead of deadlines not only ensures compliance but also enhances operational efficiency.
Mastering the Assessment and Certification Process
Obtaining CMMC certification is a rigorous process that requires meticulous planning and execution. Understanding the nuances of this process is crucial for contractors aiming to secure DoD contracts.
Steps to Secure CMMC Certification
The path to CMMC certification involves several key steps. Initially, contractors must assess their current cybersecurity posture, identifying gaps and areas for improvement. This is followed by implementing necessary controls and undergoing a third-party assessment. Successful certification hinges on thorough preparation and a commitment to continuous improvement.
The Crucial Role of the CMMC Accreditation Body
The CMMC Accreditation Body (AB) plays a vital role in maintaining the certification process's integrity. It oversees the training and certification of assessors, ensuring that assessments are conducted to the highest standards. Contractors must engage with certified assessors approved by the CMMC AB to validate their compliance efforts.
Ensuring Subcontractor Compliance
Compliance cannot be isolated to prime contractors alone. It must extend across the entire supply chain to secure sensitive information effectively.
Prime and Subcontractor Obligations
Prime contractors bear the responsibility of ensuring that their subcontractors also meet CMMC requirements. This involves establishing clear compliance expectations and conducting regular audits. Cultivating a culture of accountability can mitigate risks and protect the integrity of the supply chain.
To facilitate subcontractor compliance, prime contractors should provide resources and support to help their partners achieve certification. This collaborative approach ensures that all parties are aligned in their commitment to cybersecurity excellence.
Leveraging Resources for CMMC Success
Achieving CMMC compliance is no small feat, but a wealth of resources is available to guide contractors along the way.
Official and Third-Party Resources
The DoD offers a range of official resources, including guidance documents and training programs, to assist contractors in their compliance efforts. Additionally, numerous third-party consultants and industry experts provide valuable insights and support, helping contractors navigate the complexities of the CMMC framework.
Overcoming Common Compliance Challenges
While the road to compliance may be fraught with challenges, understanding common pitfalls can help contractors avoid them. These challenges often include resource constraints, evolving threat landscapes, and the need for ongoing training. Addressing these issues proactively can enhance a contractor's cybersecurity posture.
Looking Ahead: Global Implications and Future Trends
The impact of CMMC extends beyond U.S. borders, influencing cybersecurity practices worldwide.
The Global Reach of CMMC Compliance
As the Department of Defense (DoD) continues to emphasize the importance of cybersecurity, international contractors working with U.S. defense entities will likely need to adopt Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) standards. This global applicability underscores the universal importance of cybersecurity in safeguarding sensitive information, ensuring that all parties involved in defense contracts adhere to a unified security framework.
Adhering to these standards not only safeguards their own data but also strengthens the ongoing efforts to uphold the integrity and security of the global defense supply chain.
Anticipating Future Changes in the CMMC Landscape
CMMC is an evolving framework designed to adapt to the ever-changing cyber threat landscape. As cyber threats continue to grow in sophistication, future revisions to the CMMC are inevitable to address new vulnerabilities and strengthen existing protocols. Contractors must remain vigilant and stay informed about potential updates to the framework.
In response to these changes, contractors can proactively adapt their practices to maintain compliance and ensure their competitiveness in the defense sector. The proactive approach not only helps in safeguarding their operations but also promotes a culture of continuous improvement in cybersecurity practices.
Concluding Thoughts and Immediate Steps
In a world where cyber threats are a constant reality, CMMC represents a vital step forward in protecting our nation's defense industrial base. For defense contractors, IT security professionals, and government agencies, achieving, and maintaining CMMC compliance is not just a regulatory requirement — it's a strategic imperative.
Understanding the critical timelines, committing to ongoing improvement, and leveraging available resources, contractors can position themselves for success in a highly competitive landscape. Taking proactive steps today will not only secure DoD contracts but also fortify an organization's cybersecurity posture for the challenges of tomorrow. For further guidance or support, consider reaching out to industry experts or utilizing official CMMC resources to aid your compliance efforts.
Check out our webinar, It’s Here! DoD’s CMMC 2.0 Final Rule Explained, for important new details on CMMC 2.0!


