Spammers and phishers often forge email "from" addresses to make their email messages look legitimate. DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is a tool designed to help prevent these types of email forgeries. In this blog post, we will go over the basics of DKIM and its benefits, including how it works to authenticate email messages and how to ensure that outgoing mail servers are properly configured to use DKIM.
DKIM is an essential tool for businesses of all sizes, as it can help reduce the probability of spam messages and other forms of email fraud. Many well-known platforms and services, such as Salesforce DKIM, use DKIM to authenticate email messages and protect their users from email scams. By understanding how DKIM works and how to set it up properly, businesses can take steps to ensure that their email messages are secure and trustworthy.

DKIM Signatures and How They Work
DKIM uses digital signatures to authenticate emails. When a user sends an email from a domain, the email server signs the message using a private key. Then, a unique hash is generated from the message's contents and encrypted with the private key. Finally, the encrypted signature is added to the email header, and the email is sent to the destination.
When the recipient receives the message, their email server or messaging app retrieves the public key for the domain from the Domain Name System (DNS) records. DNS lookups are crucial in understanding how internet services work as they translate domain names to IP addresses. A TXT record is added to the domain's DNS records to store the public key:
IN TXT "v=DKIM1; p=AAAAB3Nza..."
The recipient's email server or messaging app then decrypts the signature using the public key. If the decrypted signature matches the hash generated by the sender's email server, the message is assumed to come from the claimed domain. If the signature is absent or incorrect, the message is considered a forgery or from an unknown sender.
Requirements for DKIM
While DKIM can prevent email forgeries, it has some requirements for it to work. For example, the sending email server must be configured for DKIM, and the recipient's email server must check the signature. Presently, not all email servers are configured for DKIM, and some messaging apps or email servers may not verify the signature, letting messages pass through to the recipient. As a result, spammers may still be able to forge email addresses.
Checking DKIM Signatures
Google's Gmail is an example of an email server that tries to authenticate the DKIM signatures of messages its subscribers receive. In such instances, you may see a "DKIM: 'PASS' with domain" message, which signifies that the signature was verified.
Google's Gmail does indeed try to verify the DKIM signatures of messages its subscribers receive.
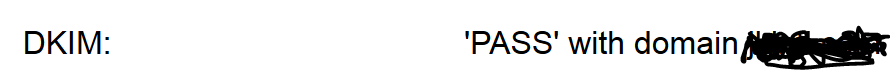
Some online sites will validate the DKIM record for a Domain.
When my mail client detects an invalid signature, I see
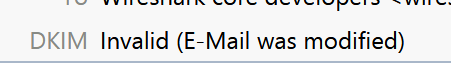
If there is no DKIM signature, there is no message.
Various online platforms can validate a domain's DKIM record, and your email client may detect invalid signatures and notify you with a "DKIM Invalid (Email was modified)" message. However, if there is no DKIM signature, there is no way to verify the message's authenticity.
Benefits of DKIM
Incorporating DKIM into a domain not only minimizes the possibility of impersonation but also bolsters the domain's credibility. As a result, small businesses can leverage the benefits of DKIM, as it is crucial for establishing trust and reducing the risk of phishing attacks.
How DNS Works with DKIM
The DNS system is fundamental to how DKIM works. DNS queries are used to look up information about a domain, such as the public key for a DKIM signature. Two types of DNS servers work together to make this possible: recursive DNS servers and authoritative name servers.
When an email server or messaging app needs to check the DKIM signature for a message, it sends a DNS query to a recursive DNS server. The recursive DNS server then sends the query to an authoritative name server for the domain. The authoritative name server provides the public key needed to decrypt the signature. Once the recursive DNS server receives the public key, it sends it back to the email server or messaging app, which can then use it to authenticate the DKIM signature.

Setting up DKIM
To set up DKIM, a domain must generate a private and public key. The public key is then stored in the domain's DNS records using a TXT record, and the private key is kept confidential. Once the domain has set up DKIM, the email server for that domain can sign outgoing messages using the private key, and the recipient's email server or messaging app can authenticate the signature using the public key.
Conclusion
In summary, DKIM is a powerful tool for preventing email forgeries and improving the credibility of sending domains. However, to work effectively, the sending email server must be configured for DKIM, and the recipient's email server or messaging app must check the signature. By understanding how DNS works with DKIM and how to authenticate DKIM signatures, you can take steps to protect your email communications and ensure that messages are coming from trusted sources.
DKIM FAQs:
What is DKIM?
DKIM stands for DomainKeys Identified Mail. It is a tool designed to prevent email forgeries by digitally signing email messages.
How does DKIM work?
- When a user sends an email from a domain, the email server signs the message using a private key.
- Then, a unique hash is generated from the message's contents and encrypted with the private key.
- The encrypted signature is added to the email header, and the email is sent to the destination.
- The recipient's email server or messaging app retrieves the public key for the domain from the DNS records and decrypts the signature using the public key.
- If the decrypted signature matches the hash generated by the sender's email server, the message is assumed to come from the claimed domain.
What are the requirements for DKIM?
The sending email server must be configured for DKIM, and the recipient's email server or messaging app must check the signature for DKIM to work effectively.
What are the benefits of DKIM?
Incorporating DKIM into a domain not only minimizes the possibility of impersonation but also bolsters the domain's credibility. It is crucial for establishing trust and reducing the risk of phishing attacks.
How does DNS work with DKIM?
DNS queries are used to look up information about a domain, such as the public key for a DKIM signature. When an email server or messaging app needs to check the DKIM signature for a message, it sends a DNS query to a recursive DNS server. The recursive DNS server then sends the query to an authoritative name server for the domain. The authoritative name server provides the public key needed to decrypt the signature.
How do I set up DKIM for my domain?
To set up DKIM, a domain must generate a private and public key. The public key is then stored in the domain's DNS records using a TXT record, and the private key is kept confidential. Once the domain has set up DKIM, the email server for that domain can sign outgoing messages using the private key, and the recipient's email server or messaging app can authenticate the signature using the public key.
How can I check the DKIM signature for a message?
Your email client may detect invalid signatures and notify you with a "DKIM Invalid (Email was modified)" message. However, if there is no DKIM signature, there is no way to verify the message's authenticity. Some online platforms can validate a domain's DKIM record.
What are some well-known platforms and services that use DKIM?
Many well-known platforms and services, such as Salesforce DKIM, use DKIM to authenticate email messages and protect their users from email scams.
This piece was originally posted Oct 12, 2021 and has been reposted with updated information, FAQ, and headers.


